Animal anatomy! Animal parts are a fascinating topic of study that can help us understand how animals interact with their environments and how they have evolved over time. From the smallest insects to the largest mammals, animals have a wide range of body parts that allow them to survive and thrive in different habitats. Some animals have specialized body parts for hunting, while others have adaptations for protection or camouflage.
In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of animal parts and learn about the different types of adaptations that animals have developed. We will look at some of the most interesting examples of animal parts, from the powerful jaws of crocodiles to the intricate eyes of insects. Whether you are a student of biology or simply have an interest in the natural world, this article will provide you with a wealth of information about the amazing diversity of animal life.
Table of Contents
Mammalian Animal Parts
Mammals are a class of vertebrate animals characterized by the presence of mammary glands that produce milk for their young. They are also distinguished by several other unique features, including hair or fur, three middle ear bones, and a neocortex in the brain.
Head
The head of a mammalian animal contains several important organs, including the brain, eyes, ears, and mouth. The skull protects the brain and sense capsules, while the eyes and ears allow the animal to perceive its environment. The mouth contains teeth and a tongue, which the animal uses to eat and communicate.
Torso
The torso of a mammalian animal contains the organs of the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems. The digestive system includes the stomach and intestines, which break down food and absorb nutrients. The respiratory system includes the lungs, which allow the animal to breathe oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. The circulatory system includes the heart and blood vessels, which transport oxygen and nutrients throughout the body.
Limbs
Mammalian animals have four limbs, which are adapted for different modes of movement. The front limbs are typically used for grasping and manipulating objects, while the hind limbs are used for running and jumping. The limbs are connected to the body by joints, which allow for a wide range of movement.
Avian Animal Parts
Birds are unique animals with distinct anatomical features that allow them to fly and thrive in their environments. Avian animal parts include their beaks, wings, and feathers, which are all essential for their survival.
Beak
The beak of a bird is a specialized structure that is used for feeding and other activities. It is made of keratin, the same material that makes up human hair and nails. The shape of the beak varies depending on the bird’s diet and lifestyle. For example, a bird that feeds on seeds will have a short, thick beak, while a bird that feeds on insects will have a long, thin beak.
Birds also use their beaks for grooming, preening, and defense. Some birds, like parrots, can use their beaks to manipulate objects and even mimic human speech.
Wings
The wings of a bird are its most distinctive feature and are essential for flight. They are made up of a complex system of bones, muscles, and feathers. The shape and size of a bird’s wings also vary depending on its lifestyle. For example, birds that soar through the air, like eagles, have long, broad wings, while birds that fly in short bursts, like sparrows, have short, rounded wings.
Birds use their wings not only for flight but also for balance, communication, and defense. Some birds, like penguins, use their wings to swim underwater.
Feathers
Feathers are another unique feature of birds and are essential for their survival. They provide insulation, protection, and help with flight. Feathers are made up of a central shaft, called the rachis, and a series of barbs that branch off from the shaft. The barbs are held together by tiny hooks called barbules, which give the feather its shape.
Feathers also play a role in communication and courtship. Male birds often have brightly colored feathers that they use to attract mates, while female birds use their feathers to blend in with their surroundings and protect their nests.
Aquatic Animal Parts
Aquatic animals are animals that live in water. They have unique adaptations that allow them to survive in their aquatic environment. These adaptations include special body parts that help them move, breathe, and protect themselves.
Fins
Fins are one of the most recognizable features of aquatic animals. They are used for movement and steering. Fins come in various shapes and sizes, and each type of fin has a specific function. For example, dorsal fins are used for stability, while pectoral fins are used for steering. Some aquatic animals, such as whales and dolphins, have evolved to have flippers instead of fins, which allow them to swim faster and more efficiently.
Gills
Gills are another important aquatic animal part. They are used for breathing underwater. Gills are specialized organs that extract oxygen from the water and release carbon dioxide. Aquatic animals with gills include fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. Gills come in various shapes and sizes, but they all work in the same way. Water flows over the gills, and oxygen is extracted from the water and absorbed into the bloodstream.
Scales
Scales are a unique feature of many aquatic animals. They provide protection from predators and help regulate body temperature. Scales come in various shapes and sizes, and each type of scale has a specific function. For example, some scales are used for camouflage, while others are used for defense. Fish are the most common aquatic animals with scales, but other animals, such as turtles and crocodiles, also have scales.
Aquatic animal parts are specialized adaptations that allow these animals to survive in their underwater environment. Fins, gills, and scales are just a few examples of the many unique features of aquatic animals. By understanding these adaptations, we can gain a better appreciation for the diversity of life in the ocean.
Insect Animal Parts
Insects are the most diverse group of animals on the planet, with over a million known species. They have a unique body structure that is divided into three parts: the head, thorax, and abdomen.
Antennae
One of the most distinctive features of insects is their antennae. These sensory organs are located on the head and are used for touch, smell, and taste. Antennae can vary greatly in size and shape depending on the species. Some insects, like butterflies, have long, thin antennae with club-like tips, while others, like beetles, have short, thick antennae with many segments.
Thorax
The thorax is the middle section of an insect’s body. It is where the legs and wings are attached. Insects have three pairs of legs, which are used for walking, jumping, and grasping. The legs are made up of several segments and are covered in tiny hairs and spines. The wings of insects are also attached to the thorax. They come in many different shapes and sizes and are used for flight, gliding, or protection.
Abdomen
The abdomen is the largest section of an insect’s body. It contains many important organs, including the digestive, reproductive, and respiratory systems. The abdomen is also where the insect’s exoskeleton is thinnest, allowing for greater flexibility. In some insects, like bees and wasps, the abdomen is modified into a stinger for defense.
Reptilian Animal Parts
Reptiles are a unique group of animals with distinct features that aid in their survival. From their scales to their tails, each part of their body serves a specific purpose.
Scales
One of the most distinctive features of reptiles is their scales. These protective coverings are made of keratin, the same material found in human hair and nails. Scales come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the species of reptile. Some are smooth, while others are rough or spiky.
Scales serve several functions for reptiles. They protect the animal from predators and environmental hazards, such as extreme temperatures and dehydration. Scales also help reptiles move more efficiently by reducing friction against surfaces.
Tail
Another important part of a reptile’s body is its tail. Tails come in different shapes and sizes depending on the species of reptile. Some are long and thin, while others are short and stubby.
Reptiles use their tails for a variety of purposes. Some species, such as geckos, can detach their tails as a defense mechanism. The tail will continue to wiggle, distracting the predator while the gecko makes its escape. Other species, such as crocodiles, use their tails as a powerful weapon to strike prey or defend themselves against predators.
In addition to defense, tails also play a role in balance and movement. Many reptiles use their tails to help them climb, swim, and run more efficiently.
Amphibian Animal Parts
Amphibians are unique creatures with distinctive features that set them apart from other animals.
Webbed Feet
One of the most recognizable features of amphibians is their webbed feet. These specialized feet are designed to help amphibians move through their aquatic habitats with ease. The webbing between their toes acts like a paddle, allowing them to swim quickly and efficiently.
Webbed feet are not just useful for swimming, however. They also help amphibians navigate through muddy or marshy areas on land. The webbing provides a larger surface area, which helps them to distribute their weight more evenly and avoid getting stuck in the mud.
Skin
Another unique feature of amphibians is their skin. Unlike other animals, amphibians do not have scales or feathers. Instead, they have moist, permeable skin that allows them to breathe through their skin. This is called cutaneous respiration.
The skin of amphibians also plays a crucial role in regulating their body temperature. Because they are cold-blooded, amphibians rely on external sources of heat to warm their bodies. Their skin helps them to absorb heat from the sun, as well as release excess heat when they need to cool down.
However, the permeable nature of amphibian skin also makes them vulnerable to environmental toxins. Polluted water and air can be absorbed through their skin, which can lead to serious health problems. This is one reason why amphibians are considered to be indicators of environmental health.
Animal Anatomy | Parts of an Animals
All animals have external structures, which means outside parts of the body. Most animals have a head, body covering, limbs, and some form of a tail. Although these body parts may look different on different animals, they are all crucial to helping them live and reproduce.
Dog Anatomy
This is a list of different body parts of a dog in English.
- Abdomen
- Back
- Belly
- Brisket
- Cheek
- Chest
- Claw
- Crest/ Neck
- Croup
- Ear
- Elbow
- Eye
- Flew
- Forearm
- Forefoot
- Forehead
- Fur
- Head
- Hock
- Leg
- Loin
- Muzzle
- Nape
- Nose
- Pasterns
- Paw
- Prosternum
- Rump
- Shoulder
- Stifle
- Stop
- Tail
- Tail Set
- Thigh
- Throat
- Tongue
- Upper Arm
- Whiskers
- Withers
- Wrist
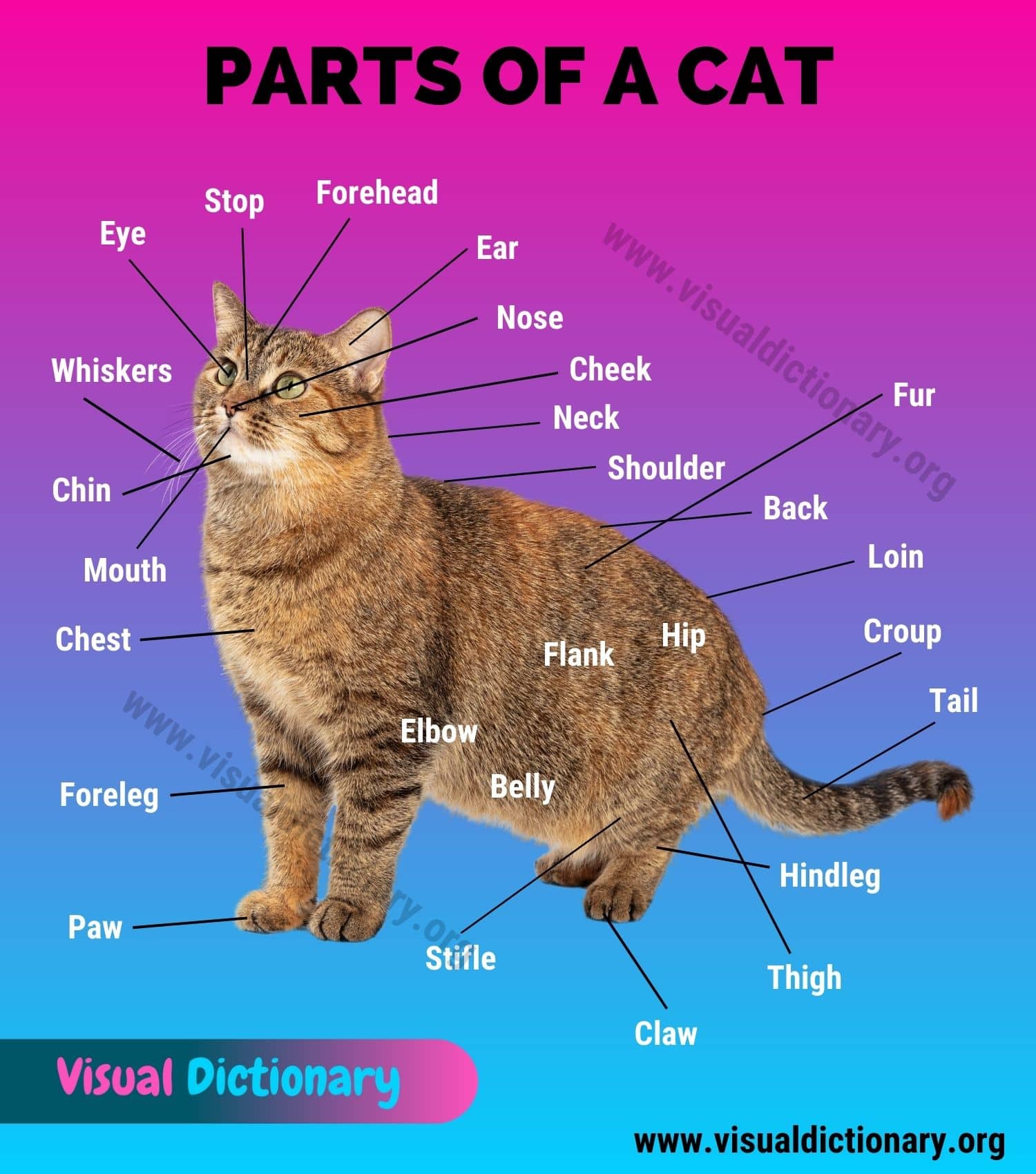
Cat Anatomy
Let’s learn different parts of a cat in English with pictures.
- Back
- Belly
- Break
- Cheek
- Chest
- Chin
- Claw
- Croup
- Doming
- Ear
- Elbow
- Eye
- Flank
- Forehead
- Foreleg
- Fur
- Head
- Hindleg
- Hip
- Hock
- Leg
- Loin
- Mouth
- Muzzle
- Neck
- Nose
- Paw
- Shoulder
- Stifle
- Stop
- Tail
- Thigh
- Tongue
- Whisker
Fish Anatomy
Fish anatomy – A useful list of external parts of a fish
- Anal fin
- Caudal fin
- Caudal peduncle
- Dorsal fins
- Eye
- Gill
- Lateral line
- Mouth
- Nostril
- Operculum
- Pectoral fin
- Pelvic fin
- Scales
- Soft-rayed
- Spiny
- Teeth
- Vent
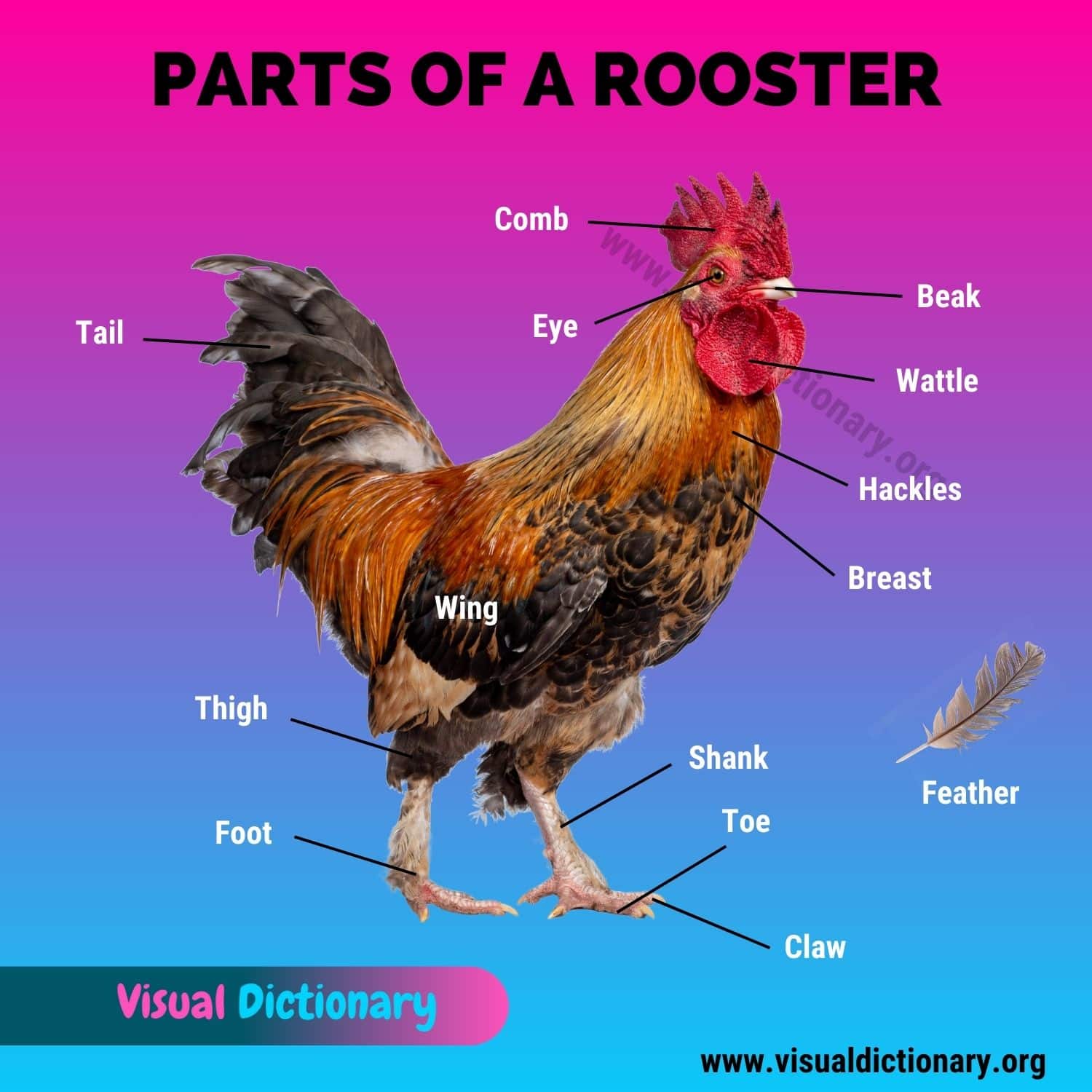
Chicken Anatomy
Chicken anatomy – We list different body parts of a rooster and a hen with pictures.
- Beak
- Breast
- Claw
- Comb
- Eye
- Feather
- Fluff
- Foot
- Hackles
- Shank
- Tail
- Thigh
- Toe
- Vent
- Wattle
- Wing
Lion Anatomy
Learn English vocabulary for lion anatomy
- Abdomen
- Back
- Chest
- Claw
- Ear
- Eye
- Flanks
- Foreleg
- Fur
- Head
- Hind leg
- Jaw
- Mane
- Mouth
- Muzzle
- Neck
- Nose
- Paw
- Rump
- Shoulder
- Tail
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Underbelly
- Whiskers
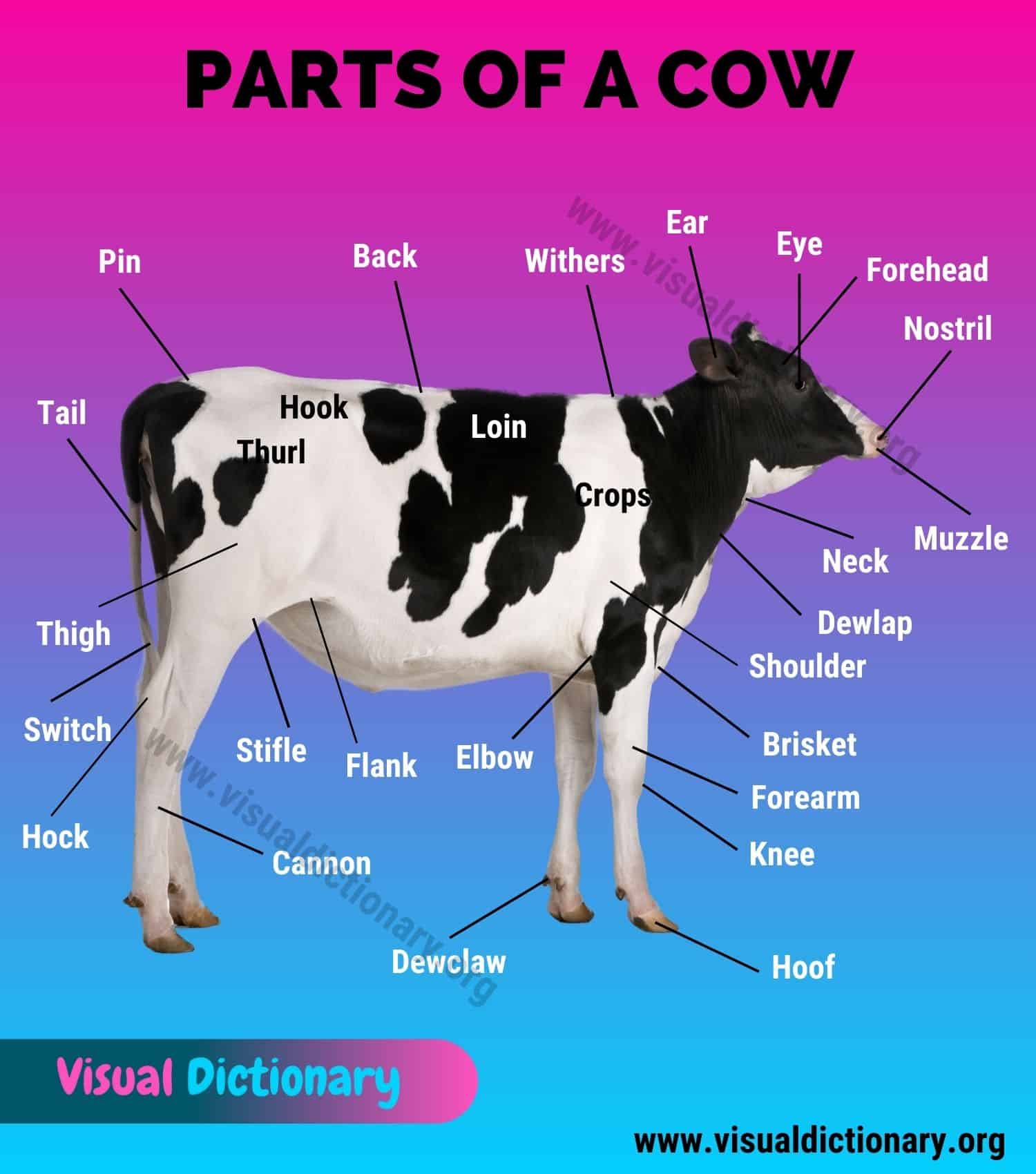
Cow Anatomy
Below is an excellent list of parts of a cow with a picture.
- Back
- Brisket
- Cannon
- Dewclaw
- Dewlap
- Ear
- Elbow
- Eye
- Flank
- Fore udder
- Forearm
- Forehead
- Heel
- Hock
- Hoof
- Hook
- Horn
- Knee
- Leg
- Loin
- Muzzle
- Neck
- Nostril
- Pin
- Rump
- Shoulder
- Stifle
- Switch
- Tail
- Teat
- Thigh
- Thurl
- Toe
- Tongue
- Withers
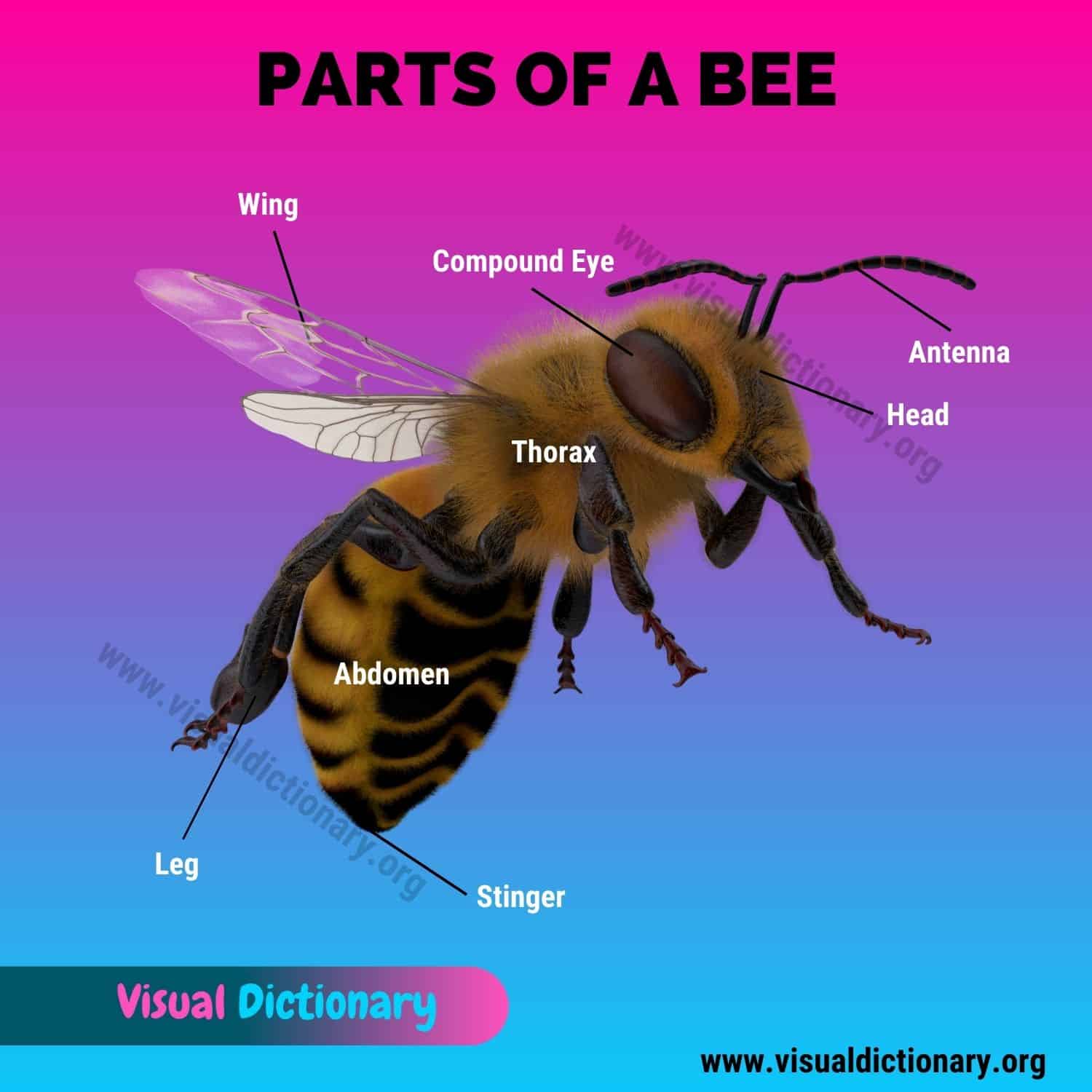
Bee Anatomy
Learning about parts of a bee in English
- Abdomen
- Antenna
- Compound Eye
- Foreleg
- Forewing
- Head
- Hind Leg
- Hindwing
- Mandibles
- Middle Leg
- Spiracle
- Stinger
- Thorax
- Tongue
Horse Anatomy
Horse anatomy – An interesting external parts of a horse
- Back
- Barrel
- Cannon
- Chestnut
- Chin Groove
- Coronet
- Crest
- Croup
- Dock
- Elbow
- Ergot
- Fetlock
- Flank
- Forearm
- Forehead
- Gaskin
- Heel
- Hock
- Hoof
- Knee
- Loin
- Muzzle
- Pastern
- Point of Hip
- Poll
- Shoulder
- Stifle
- Tail
- Throat Latch
- Withers
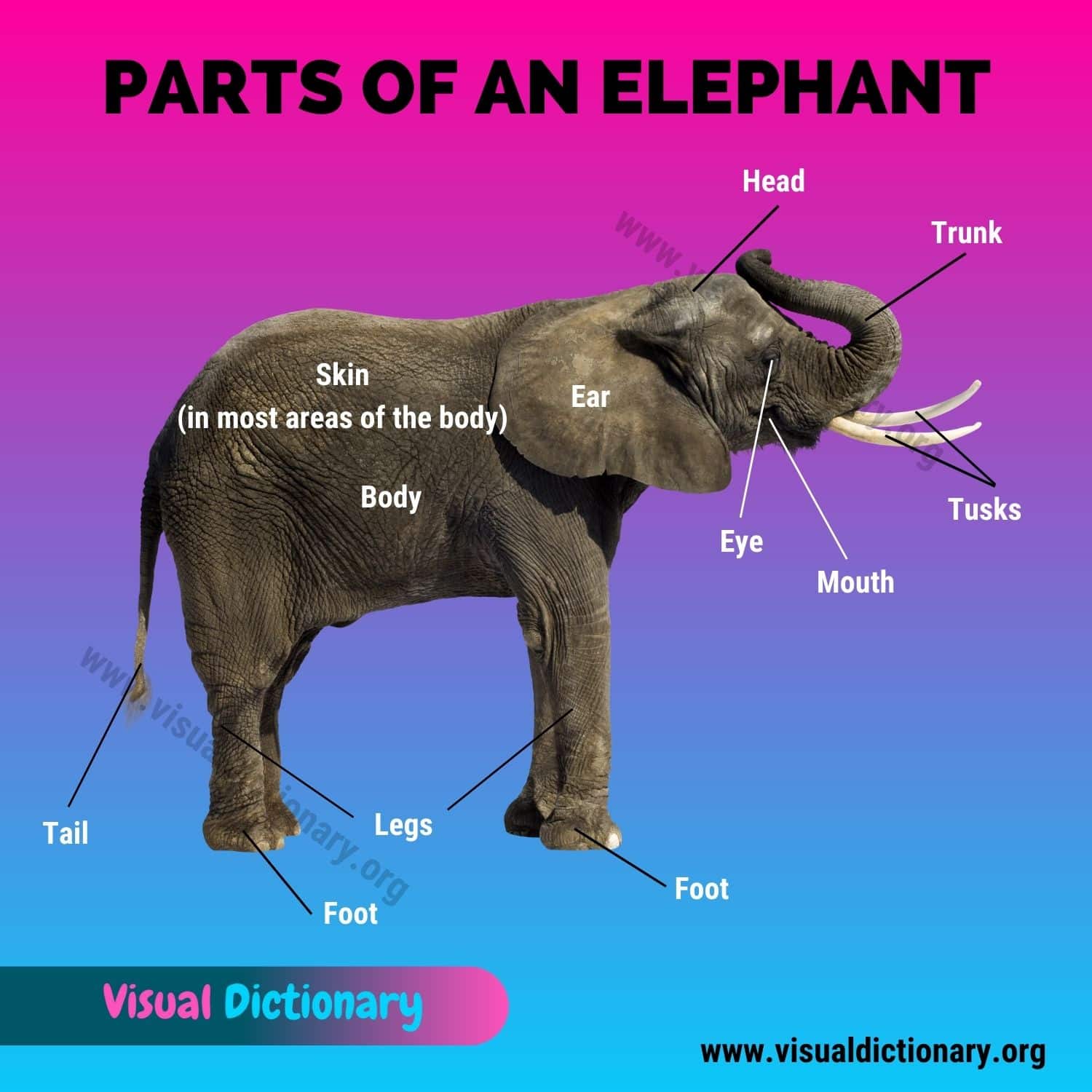
Elephant Parts
Here are common elephant parts.
- Body
- Ear
- Eye
- Foot
- Head
- Head
- Leg
- Mouth
- Skin
- Tail
- Trunk
- Tusk
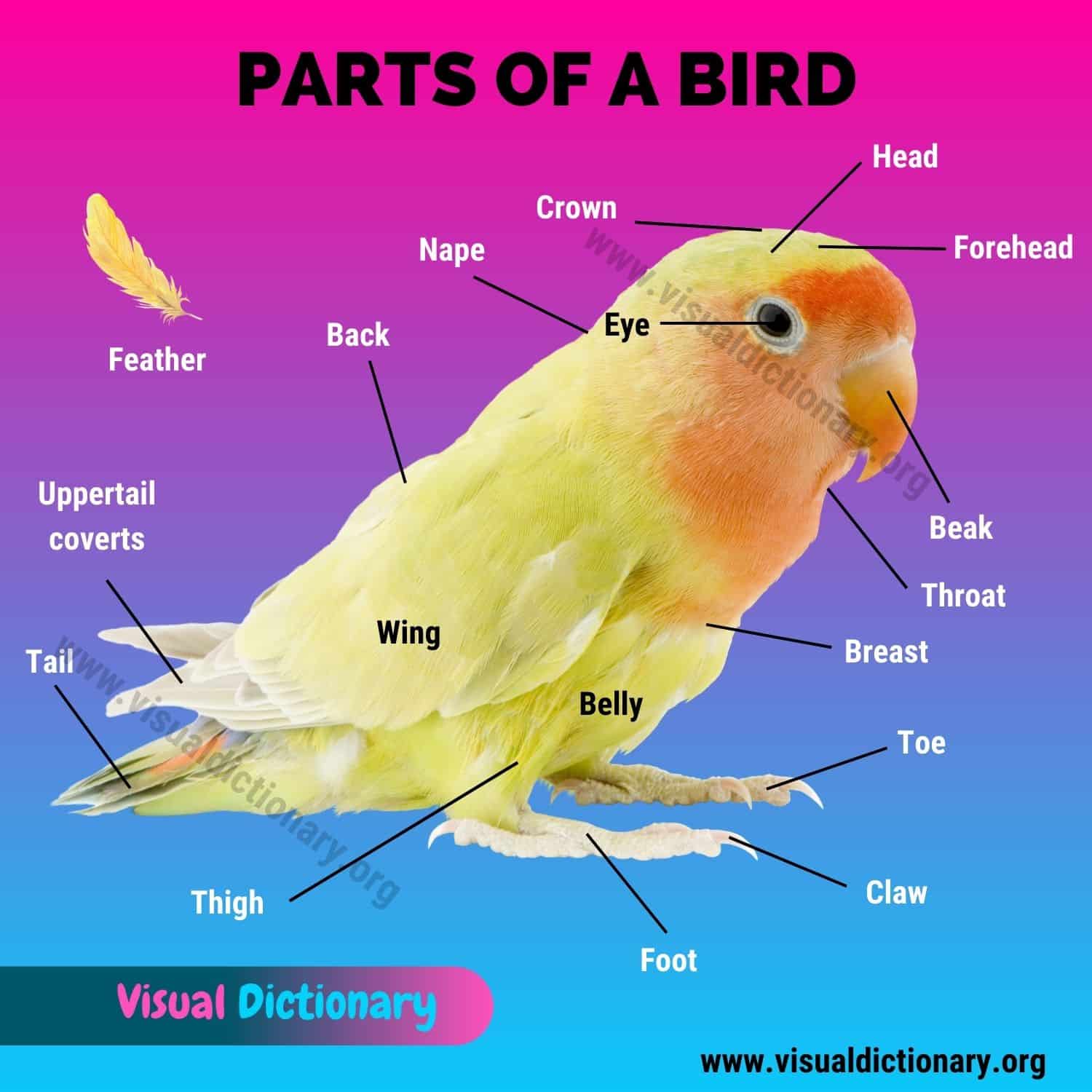
Bird Anatomy
Bird anatomy – This is a useful list of external parts of a bird.
- Back
- Beak
- Belly
- Breast
- Chin
- Claw
- Crown
- Eye
- Feather
- Foot
- Forehead
- Head
- Nape
- Rump
- Tail
- Thigh
- Throat
- Toe
- Uppertail coverts
- Wing
Parts of an Animals
- Parts of a Bird
- Parts of a Crab
- Parts of a Goat
- Parts of a Pig
- Parts of a Horse
- Parts of a Cow
- Parts of a Lion
- Parts of a Dog
- Parts of a Cat
- Parts of a Tiger
- Parts of an Elephant
- Parts of a Chicken
- Parts of a Duck
- Parts of a Crab
- Parts of a Turtle
- Parts of a Fish
FAQs on Animal Anatomy
What is the structure of an animal’s body?
The structure of an animal’s body is composed of different parts that work together to help the animal survive. These parts include bones, muscles, organs, and tissues. The body of an animal is divided into different regions, including the head, thorax, abdomen, and limbs.
What are the external parts of an animal’s body?
The external parts of an animal’s body are the parts that are visible on the outside. These include the skin, fur, feathers, scales, and claws. These external parts help animals to adapt to their environment and protect them from predators.
What are the parts of an animal’s head?
The parts of an animal’s head include the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and brain. These parts help animals to sense their environment, communicate with other animals, and find food.
What are some special body parts that animals have?
Some animals have special body parts that are adapted to their environment. For example, birds have wings that allow them to fly, while fish have gills that allow them to breathe underwater. Some animals also have specialized teeth or claws that help them hunt for food.
What are the functions of different animal body parts?
Different animal body parts have different functions. For example, the heart pumps blood throughout the body, while the lungs help animals breathe. The digestive system helps animals break down food and extract nutrients, while the reproductive system allows animals to reproduce and pass on their genes.
What are the common body parts found in animals?
The common body parts found in animals include the brain, heart, lungs, digestive system, and reproductive system. These parts are essential for the survival and reproduction of animals.