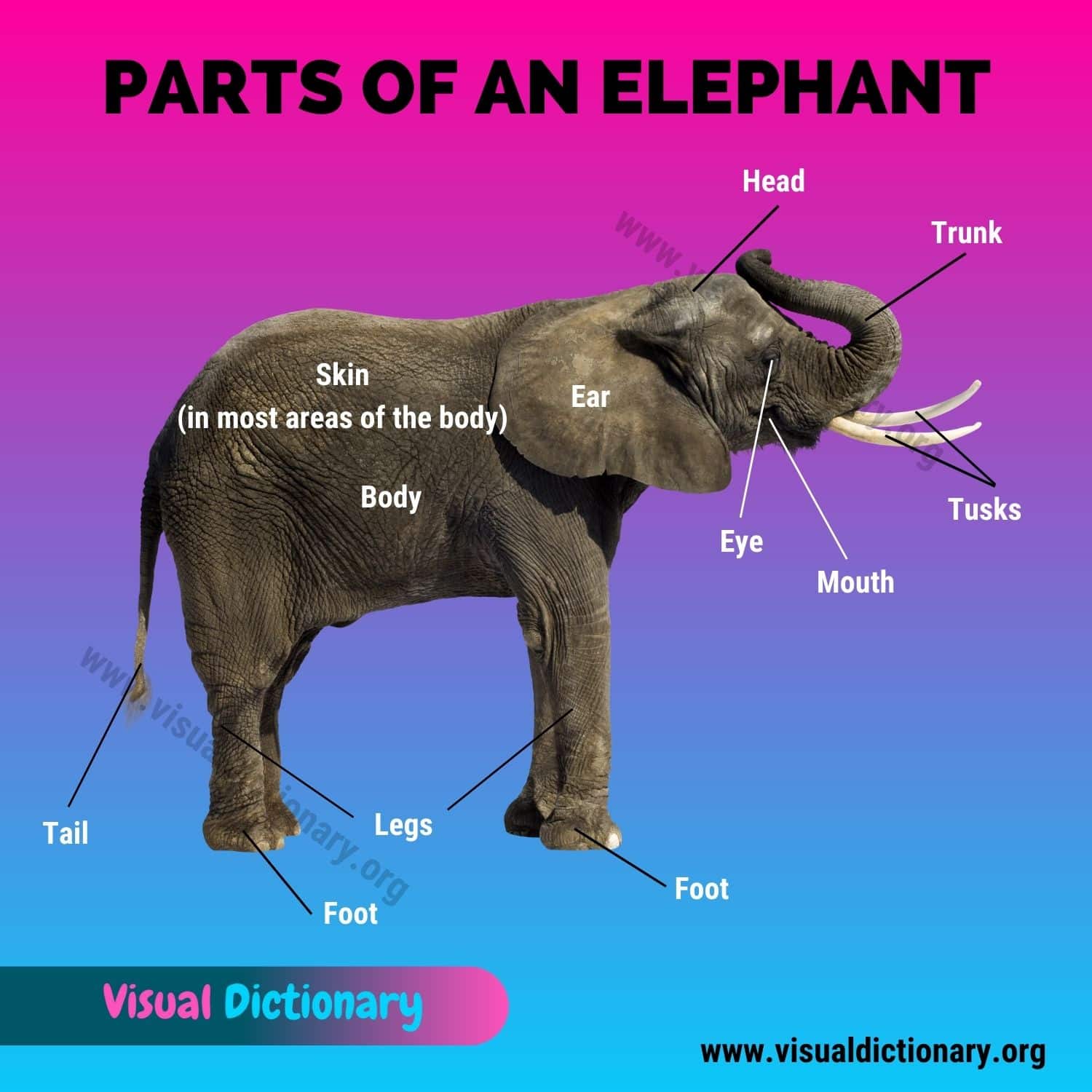
Have you ever wondered about the different parts of an elephant? These majestic creatures are known for their large size and unique features, but what makes up their anatomy? In this article, we will explore the various parts of an elephant and their functions.
Table of Contents
Elephants
Elephants are the largest land animals on Earth, and their anatomy is nothing short of remarkable. They are known for their unique physical characteristics, which make them stand out from other animals.
Body Size and Shape
The elephant’s body is massive and bulky, with a round belly and a wide back. They can grow up to 13 feet tall and weigh up to 22,000 pounds. Male elephants are typically larger than females, with longer tusks and a more prominent forehead.
Trunk
One of the most distinctive features of an elephant is its trunk. The trunk is a multi-functional organ with over 40,000 muscles. Its primary functions are for breathing, smelling, touching, and grasping. Elephants also use their trunks to drink water, which they then squirt into their mouths, and they can even use their trunk as a snorkel when swimming.
Tusks
Elephants have two long, curved tusks made of ivory that protrude from their upper jaw. Tusks are used for root digging, brush clearing, fighting over females, and self-defense. They also protect their trunks, which are an important part of an elephant’s body.
Ears
The elephant’s large ears are one of its most distinguishing characteristics. Elephants use their ears to regulate their body temperature, as well as to communicate with other elephants. They can also use their ears to detect sounds from long distances.
Skin
Elephants have thick, wrinkled skin that is gray in color. Their skin is as thin as paper, but it provides a protective function for all animals. However, there are some unique characteristics about the elephant’s skin. For example, elephants have sparse hair on their skin and their skin is covered in a layer of dust and mud to protect them from the sun.
Elephant Parts
Elephants are the largest grassland animal in the world. They can hear with their feet and live an average of 70 years.
Trunk
An elephant’s trunk is one of its most distinctive features. It is a long, muscular appendage that serves many functions, including breathing, smelling, touching, grasping, and making sounds. The trunk is made up of over 100,000 muscles and can be up to 2 meters long. Elephants use their trunks to drink water, pick fruits, and even to spray themselves with dust or mud to keep cool.
Tusks
Elephant tusks are elongated incisor teeth that protrude from the upper jaw. Tusks are used for a variety of purposes, including defense, digging, and foraging. Tusks can grow up to 3 meters long and can weigh over 100 kilograms. Unfortunately, elephants are often hunted for their tusks, which are highly valued in some cultures for their ornamental and medicinal properties.
Teeth
Elephants have six sets of teeth throughout their lives, but they only have two or three teeth in their mouth at any given time. As their front teeth wear down, they are replaced by new teeth that move forward to take their place. This process continues throughout their lives, and when they run out of teeth, they can no longer chew their food properly and may die of starvation.
Legs and Feet
Elephants have four legs that are very strong and sturdy. Their feet are wide and cushioned, which helps them to distribute their weight evenly and walk quietly. Elephants walk on their toes, which are covered by thick, calloused pads. They also have a fifth toe, which is located higher up on their leg and is used for balance and support.
Parts of An Elephant | List
- Eye
- Head
- Ear
- Trunk
- Mouth
- Foot
- Leg
- Tail
- Tusk
- Head
- Body
- Skin
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the body parts of an elephant and their uses?
Elephants have many body parts that help them survive in their natural habitat. Some of the most important body parts include their trunks, tusks, ears, and feet. Elephants use their trunks for a variety of tasks, such as breathing, smelling, and grabbing food. Their tusks are used for defense and to dig for food and water. Their large ears help them regulate their body temperature, and their feet are used for walking long distances and foraging for food.
What are 5 characteristics of an elephant?
Elephants are known for their intelligence, social behavior, communication skills, and memory. They also have a unique ability to use tools and to show empathy towards other elephants and even other species. Elephants are also known for their long lifespans, with some living up to 70 years in the wild.
What are the physical features of an elephant?
Elephants are characterized by their large size, gray skin, and long trunks. They also have large ears that they use to regulate their body temperature, and their tusks can grow up to 10 feet long. Elephants have four legs and large, flat feet that help them walk long distances and forage for food.
Why is an elephant’s skin so thick?
An elephant’s skin is very thick and tough, which helps protect them from predators and the harsh elements of their environment. Their skin is also wrinkled, which helps them retain moisture and stay cool in hot weather.
What are some uses of an elephant’s tusk?
Elephants use their tusks for a variety of tasks, such as digging for food and water, defending themselves from predators, and foraging for food. Unfortunately, elephants are also hunted for their tusks, which are made of ivory and are highly valued in some cultures.
How does an elephant use its trunk?
An elephant’s trunk is a highly versatile tool that they use for a variety of tasks. They can use it to breathe, smell, grab food and water, and even communicate with other elephants. Elephants can also use their trunks to make loud trumpeting sounds, which they use to communicate with other elephants over long distances.
Related terms: